The Motivation
This is an API from an imaginary university database in one of the courses to help me understand more about how to use Express.js and MongoDB to create an API.
Database Design
Below are the collection of the database and its design
CoursesStudentCourseScoresSemestersStudentsTeachers
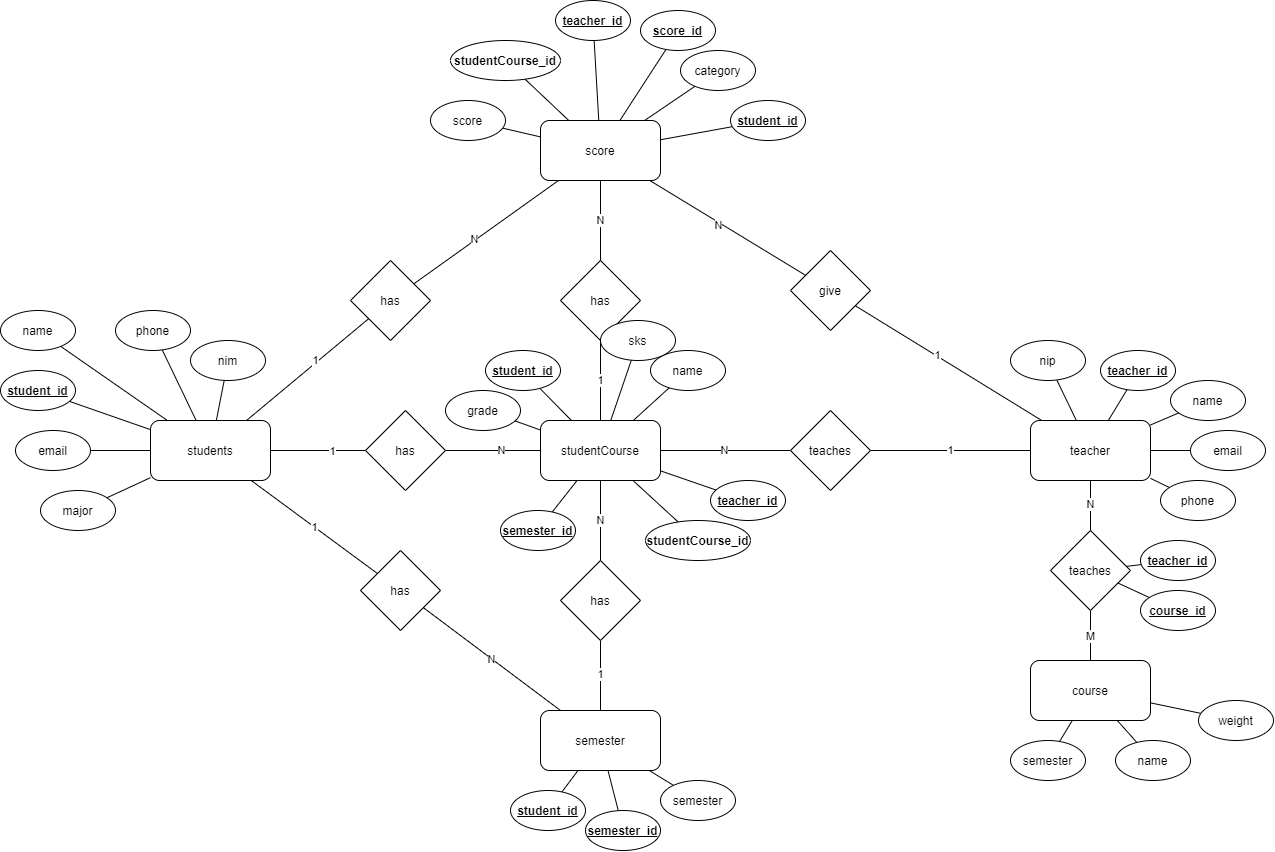
The Thought Process
MongoDB is a flexible DBMS. Unlike SQL DBMS in general which has standard rules. In NoSQL the data model will greatly affect the optimality and performance of the database. So I will try to explain why I designed the database like the picture above.
Many-to-many relationship in NoSQL was quite difficult for me. I thought, maybe if I use the many-to-many rules of SQL, i.e. create 3 tables/collections, where the 3rd table/collection is used to relate the two, then what’s the point of me learning NoSQL if I end up falling back on SQL rules, even if it’s allowed. At first I was also confused about how to design the json response that would later be displayed, even though the most important thing should be the query from the database so that it produces the desired result and performance.
My way of thinking is, because NoSQL is flexible, instead of creating a 3rd table like SQL rules in general, I thought why not just create the 3rd table without creating 3 tables. This way of thinking explains why the Student and Semester collections have a one-to-many relationship. Even though that will make the total of documents in the Semester collection n x m, where n is Student, m is Semester. But in my opinion it doesn’t matter because the 3rd table in SQL many-to-many relationship also applies like that. More importantly, the payload that’s returned when fetching data from a collection is minimal because of this method. If I use a many-to-many relationship by relating many students to documents in a semester, where one Course can have hundreds or even thousands of students, this will result in a decrease in performance while querying the data. This also applies to the relationship between StudentCourse and Semester, where in 1 semester there must be many Courses and in 1 Course can be in many Semesters. This relationship also applies to Teacher and StudentCourse relationships.
In the Score-Student and Score-StudentCourse relationships it is correct to use one-to-many because a specific exact score is owned by one student and also one course. Why are there 2 collections that are almost the same name, Course and StudentCourse?. Course is useful as a list of courses if students want to program their course plans for certain semester. This is also useful as a many-to-many relationship in the Teacher collection as lecturers that teach the specific course. The StudentCourse collection is useful as a sort of 3rd table. To add courses, first select a course from the list in the Course collection. Once selected, we duplicate the data in StudentCourse when adding the document to track what Course that already be taken by a specific student.
Documentation
Data Addition
Adding data can be done using the POST method on the URI:
http://localhost/collectionNameExample : http://localhost/students
Data Searching
Searching for data can be done using the GET method on the URI:
http://localhost/collectionName/search?req.queryExample : http://localhost/students/search?_id=q8ownfw98y
Data Editing
Data editing can be done using the PATCH method on the URI :
http://localhost/collectionName/:id_collectionNameExample : http://localhost/students/0q7e87q97e
Data Deletion
To delete one document, you can use the DELETE method on the URI:
http://localhost/collectionName/:id_collectionNameExample : http://localhost/students/0q7e87q97e
Meanwhile, the deletion of the entire document can be done on the URI
http://localhost/collectionNameExample : http://localhost/students
Document Relationship
To make relationship between documents, you can use the PATCH method on the URI:
http://localhost/collectionName_from/assign/collectionName_destination/:id_collectionName_from?req.query_collectionName_destinationExample: http://localhost/semesters/assign/student/s8ha9dsh?nim=195150400111034
Deleting Document Relations
To remove the relationship between documents, you can use the PATCH method on the URI:
http://localhost/collectionName_from/unassign/collectionName_destination/:id_collectionName_from?req.query_collectionName_destinationExample: http://localhost/semesters/unassign/student/s8ha9dsh?nim=195150400111034
How to Use the API
To use the API, it is recommended to add data to the Courses collection without having to relate it to other documents using the POST method for the initial data in the URI:
http://localhost/courseOnce filled in, then we fill in the data in the Teachers and Students collection because universities also need students to teach, and lecturers as teaching staff. Data entry can be done using the POST method via the URI:
http://localhost/students
http://localhost/teachersWays for Students to Program Their Study Plans for the Next Semester
First, add a semester for students. Adding semesters can be done by using the POST method on the URI:
http://localhost/semestersThen relate that semester to students who want to program their study plans for that semester using the PATCH method on the URI:
http://localhost/semesters/assign/student/:id_semester?req.query_studentand enter the query using the _id of the intended student. After that create a program to select a course from the course data, which will later be added to the StudentCourse Collection as a document by using the POST method on the URI :
http://localhost/studentCoursesAfter that, you can add the selected course in the semester that has been related to the student earlier by using the PATCH method on the URI below and enter a query using the _id of the course and the intended semester:
http://localhost/studentCourses/assign/semester/:id_studentCourse?req.params_semester
http://localhost/studentCourses/assign/student/:id_studentCourse?req.params_studentHow to assign lecturers to a course
In this case, we are relating the lecturer to a static document in the Courses collection. The goal is as an option to be displayed by any lecturer who is in charge of a course. So that we can assign lecturers to a course by relating them using the PATCH method on the URI below and entering queries using the id of the intended course and teacher:
http://localhost/teachers/assign/course/:id_teacher?req.params_course
http://localhost/courses/assign/teacher/:id_course?req.params_teacherHow to assign a lecturer to teach a course for a student
After the assignment is complete, we need to assign a lecturer to teach a course to a student. To assign it, associate StudentCourse with the lecturer using the PATCH method on the URI below and enter a query using the id of the target teacher. :
http://localhost/studentCourses/assign/teacher/:id_studentCourse?req.params_teacherThe way lecturers give grades to students in a course
First, add data to the Scores collection. Scores on a course can be more than one. Then add the necessary score documents for a course. Adding data can be done using the POST method on the URI:
http://localhost/scoresThen relate the score to the StudentCourse document using the PATCH method on the URI below and enter a query using the id of the target score. :
http://localhost/scores/assign/course/:id_score?req.params_studentCourseNext, also associate who the lecturer gave the score to by using the PATCH method on the URI:
http://localhost/scores/assign/teacher/:id_score?req.params_teacherand enter the query using the id of the target score. Finally, associate it to the student concerned using the PATCH method on the URI below and enter a query using the id of the target score.:
http://localhost/scores/assign/student/:id_score?req.params_student